Match Fixing Hasn't Slowed. What’s New: AI Is Watching

The battle against match fixing around the world is increasingly using the exploding world of artificial intelligence.
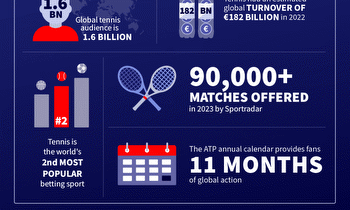
Sports data company Sportradar on Monday released the results of its annual integrity report, findings coming from active monitoring of about 850,000 events across 70 sports last year and particularly the betting lines around those events. The overall results were essentially even with those for 2022, with suspected manipulation found in 0.21% of events, or one in every 467. But what did materially change was the use of AI, with that technology assisting in 73% of the flagged events.
That percentage more than doubled compared to 2022.
AI has been integrated in Sportradar’s fraud detection systems since 2018. But far beyond just sports, AI technology over the past year has hit a certain inflection point in its power and scale, perhaps most notably seen through the meteoric ascent of generative AI systems like ChatGPT and Gemini, that can create a wide range of content based on user prompts. For Sportradar, in particular, the efforts to detect match fixing in part involve AI analysis of more than 30 billion real-time odds changes and consumer betting activity across 600 global betting operators.
Andreas Krannich, Sportradar’s executive vice president of integrity, rights protection, and regulatory services, said that ongoing AI model advancements will “enhance efforts against match fixing” and help safeguard sports from manipulation.
Though obviously a distinct minority of all games played, match fixing remains a paramount concern for every pro sports league and governing body. The NFL, which is aligned with key Sportradar competitor Genius Sports, dealt with this last year as it heightened its range of penalties to players violating league policies, including the leaking of inside information to bettors.
Most of Sportradar’s flagged events came from outside of North America, with Europe, Asia, and South America combining for 1,186 of the company’s 1,329 suspicious matches. Just 35 were from North America. Overall, though, this data from Sportradar resulted in 147 sporting and criminal sanctions spanning 10 sports across 23 countries.